It supports various output methods by output-plugins. It has got completely configurable keybindings and it can be controlled from the outside via cmus-remote(1).
Tuesday, November 26, 2013
Monday, November 25, 2013
How to Protecting Against SYN Flood Attacks
In Windows, a protection allowing to detect and adjust the time when system is being targeted with a SYN flood attack, i.e., a type of denial of service attack. When the protection is enabled, responses of this connection time out more quickly in the event of an attack.
How To Secure Windows XP
Windows XP offers wonderful security features and as an administrator
of the network or the computer it’s your responsibility to check the
system’s security from every aspect.
In this article you will learn that how to implement the security procedures in the Windows XP Professional environment. There is not a single method, software or hardware that can protect your computer from internal and external security threats. Before you determine the security strategy you need to understand that what the security risks are.
Due to the poor default settings, Windows XP has some security holes and these holes can be fixes by implementing the security procedures. Some of the major security procedures that can be configured and implemented in the Windows XP Professional are following.
In this article you will learn that how to implement the security procedures in the Windows XP Professional environment. There is not a single method, software or hardware that can protect your computer from internal and external security threats. Before you determine the security strategy you need to understand that what the security risks are.
Due to the poor default settings, Windows XP has some security holes and these holes can be fixes by implementing the security procedures. Some of the major security procedures that can be configured and implemented in the Windows XP Professional are following.
How to disable Administrative shares on Windows XP
- Open Registry Editor (Start - Run - type "regedit" and press OK button)
- Navigate to "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanManServer\Parameters"
- Right click on "AutoShareWks" and change its value to "0"
How To Renaming the Administrator account in Windows XP
The Administrator account exists on all computers runningWindows XP Professional and Home. This gives potential hackers, half theinformation they need to access your computer—all they have to do is guess yourpassword.
You can make it more difficult for unauthorized persons toget into your system by renaming the Administrator account.
Sunday, November 24, 2013
See Bandwidth Usage Per Process Via Terminal with Nethogs
NetHogs is a small 'net top' tool. Instead of breaking the traffic down per protocol or per subnet, like most tools do, it groups bandwidth by process.
NetHogs does not rely on a special kernel module to be loaded. If there's suddenly a lot of network traffic, you can fire up NetHogs and immediately see which PID is causing this. This makes it easy to indentify programs that have gone wild and are suddenly taking up your bandwidth.
NetHogs does not rely on a special kernel module to be loaded. If there's suddenly a lot of network traffic, you can fire up NetHogs and immediately see which PID is causing this. This makes it easy to indentify programs that have gone wild and are suddenly taking up your bandwidth.
Saturday, November 23, 2013
Xtreme Download Manager for Windows
Friday, November 22, 2013
Startup Repair Infinite Loop Recovery
How to Recover from an Infinitely Looping Startup Repair Loop without Reinstalling Windows.
If you've ever experienced a Startup Repair that continously loops and fails to fix the problem of not being able to load windows, even in safe mode, then you'll know that usually the only way to recover from this when System Restore does not work is to do a clean install of Windows.This tutorial will show you how to use the System Recovery Options provided by Windows to recover your system to a working state so that you don't have to risk losing data by performing a clean install.
Warning: The instructions presented withing this tutorial must be followed correctly, or you can damage your Windows 7 installation even further. This tutorial is designed to help recover from a bad registry that is causing the startup repair loop. You should note that there may still be some issues remaining that cannot be fixed by manually restoring the registry.
Autoruns Programs Viewer for Windows
Introduction
This utility, which has the most comprehensive knowledge of auto-starting locations of any startup monitor, shows you what programs are configured to run during system bootup or login, and shows you the entries in the order Windows processes them. These programs include ones in your startup folder, Run, RunOnce, and other Registry keys. You can configure Autoruns to show other locations, including Explorer shell extensions, toolbars, browser helper objects, Winlogon notifications, auto-start services, and much more. Autoruns goes way beyond the MSConfig utility bundled with Windows Me and XP.Autoruns' Hide Signed Microsoft Entries option helps you to zoom in on third-party auto-starting images that have been added to your system and it has support for looking at the auto-starting images configured for other accounts configured on a system. Also included in the download package is a command-line equivalent that can output in CSV format, Autorunsc.
YUMI (Multiboot USB Creator)
YUMI (Your Universal Multiboot Installer), is the successor to our
MultibootISOs. It can be used to create a Multiboot USB Flash Drive
containing multiple operating systems, antivirus utilities, disc
cloning, diagnostic tools, and more. Contrary to MultiBootISOs which
used grub to boot ISO files directly from USB, YUMI uses syslinux to
boot extracted distributions stored on the USB device, and reverts to
using grub to Boot Multiple ISO files from USB, if necessary.
Aside from a few distributions, all files are stored within the Multiboot or yumi folder (depending on version), making for a nicely organized Multiboot USB Drive that can still be used for other storage purposes.
Creating a YUMI Multiboot MultiSystem Bootable USB Flash Drive
YUMI works much like Universal USB Installer, except it can be used to install more than one distribution to run from your USB. Distributions can also be uninstalled using the same tool!
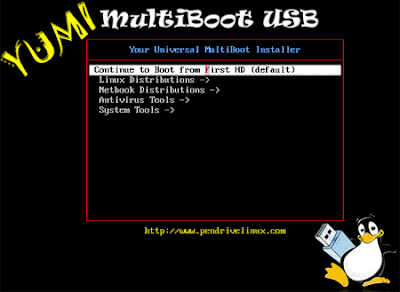
YUMI's Main Multiboot Boot Menu
Aside from a few distributions, all files are stored within the Multiboot or yumi folder (depending on version), making for a nicely organized Multiboot USB Drive that can still be used for other storage purposes.
Creating a YUMI Multiboot MultiSystem Bootable USB Flash Drive
YUMI works much like Universal USB Installer, except it can be used to install more than one distribution to run from your USB. Distributions can also be uninstalled using the same tool!
YUMI's Main Multiboot Boot Menu
Installing and Removing Nmap on Linux
Introduction
Nmap can often be installed or upgraded with a single command, so don't let the length of this chapter scare you. Most readers will use the table of contents to skip directly to sections that concern them. This chapter describes how to install Nmap on many platforms, including both source code compilation and binary installation methods. Graphical and command-line versions of Nmap are described and contrasted. Nmap removal instructions are also provided in case you change your mind.File Permissions (chmod) on Linux
chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file.
Usage:
Or
Usage:
When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that you are setting permissions for. Therefore, when setting permissions, you are assigning them for "yourself", "your group" and "everyone else" in the world. These users are technically know as:
Usage:
chmod permissions file
Or
Usage:
chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file
When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that you are setting permissions for. Therefore, when setting permissions, you are assigning them for "yourself", "your group" and "everyone else" in the world. These users are technically know as:
- Owner
- Group
- World
MAC Address Spoofing on Linux
There are two methods for spoofing a MAC address using either iproute2 (installed by default) or macchanger (available on the official repositories).
Both of them are outlined below.
The section that interests us at the moment is the one that has "link/ether" followed by a 6-byte number. It will probably look something like this:
Both of them are outlined below.
Method 1: iproute2
First, you can check your current MAC address with the command:
# ip link show
where interface is the name of your network interface.The section that interests us at the moment is the one that has "link/ether" followed by a 6-byte number. It will probably look something like this:
link/ether 00:1d:98:5a:d1:3a
The first step to spoofing the MAC address is to bring the network interface down. It can be accomplished with the command:
# ip link set dev interface down
Next, we actually spoof our MAC. Any hexadecimal value will do, but some networks may be configured to refuse to assign IP addresses to a client whose MAC does not match up with a vendor. Therefore, unless you control the network(s) you are connecting to, it is a good idea to test this out with a known good MAC rather than randomizing it right away.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)







.jpg)